Product docs and API reference are now on Akamai TechDocs.
Search product docs.
Search for “” in product docs.
Search API reference.
Search for “” in API reference.
Search Results
results matching
results
No Results
Filters
Use nano to Edit Files in Linux
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
GNU nano, or more commonly, nano is the basic, built-in editor for most Linux distributions. In this QuickAnswer, we’ll cover some of the essentials to help you get started.
To learn more, visit our full guide on using nano .
Use nano to Open a System File
From the terminal, enter nano and the file name. If the file doesn’t exist, nano will create a new, temporary version in the location you specify. In this example, we’ll use sudo permissions to open the system’s hosts file:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
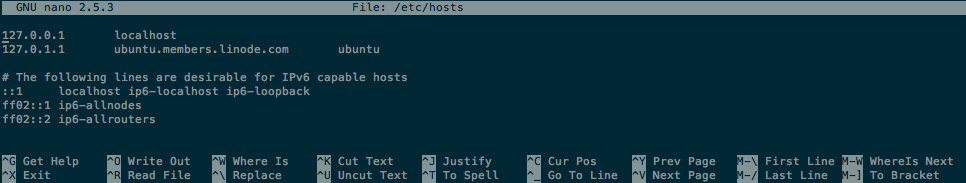
The above example opens the system hosts file, similar to the following:

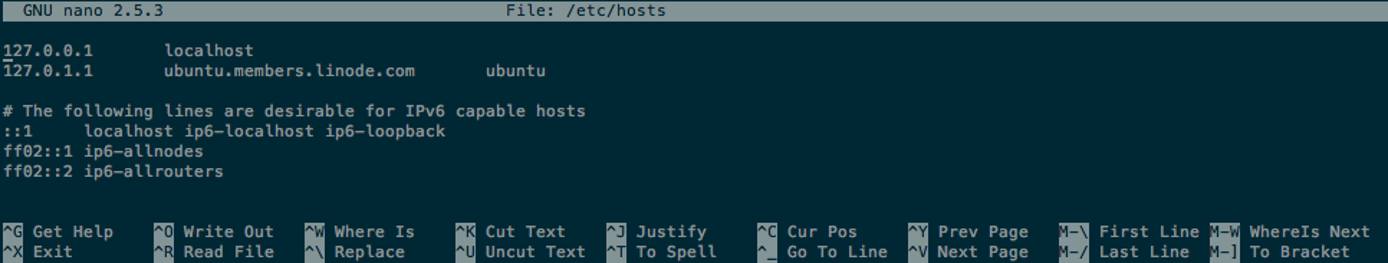
In the default view, nano displays the file being edited in the center of the top Titlebar. At the bottom, the Shortcut List shows commonly used commands where ^ stands for the CTRL key. To save, hold CTRL and press O (for Write Out); to exit, CTRL+X.
Notice that some commands induce the Statusbar, at the bottom, directly above the Shortcut List. For example, the Statusbar appears when saving files and running searches (CTRL+W).
Helpful nano Shortcuts
- ^W: Search within the open file
- ALT+W: Find the next instance of the search
- ^O: Save the file
- ^K: Cut the entire line
- ^U: Paste the entire line
- ^T: View the file browser
- ^X: Exit
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on